AstroGuider overview
AstroGuider is along with AstroImager, AstroDSLR and AstroTelescope part of powerful, but still easy to use astrophotography suite for Apple Mac computers built around INDIGO and INDI standard. Even if they can be used separately, they are meant to work together and with other astronomy and astrophotography tools for macOS or iOS provided by CloudMakers, like INDIGO Server for macOS, INDIGO Control Panel, FITS Preview, iINDI or NightSky Toolbox.
Specific purpose of AstroGuider is to control the guiding camera, its guider port and/or the connected mount. It can be calibrated semi-automatically or manually, you do not need to take care about camera orientation or pixel scale.
It can control many devices supported by built-in INDIGO drivers or it can use any 3rd party INDIGO or INDI driver. Out-of-the-box it contains INDIGO drivers for the following cameras, mounts and guiding devices:
- Simulator drivers,
- Atik CCD driver (Titan, 3xx/4xx/One/16200, VS/Infinity, 11000/4000),
- StarlightXpress CCD,
- SSAG/QHY5 CCD driver,
- ZWO ASI CCD and USB-ST4 guider drivers,
- IIDC CCD driver (compatible USB 2.0+ or FireWire cameras, including Atik GP),
- SBIG CCD driver (vendor SDK must be installed),
- Moravian Instruments CCD driver,
- Meade DSI CCD driver,
- QHY CCD and wheel driver (experimental, unstable),
- AltairAstro CCD driver,
- ToupTek CCD driver,
- EQMac driver,
- CGUSBST4 guider driver,
- GPUSB guider driver,
- LX200 compatible mount driver,
- NexStart compatible mount driver,
- Takahashi Temma mount driver,
- iOptron mount driver.
To use Atik cameras, make sure that ArtemisHscService is not running (installed e.g. as a part of Nebulosity4 or TheSkyX).
What's new in version 3.8
- INDIGO framework updated to 2.0.76,
- Issue with USB devices on pre-Mojave systems fixed.
What's new in version 3.6
- INDIGO framework updated to 2.0.75,
- AltairAstro and ToupTek driver added,
- more Mojave dark appearance cleanup.
What's new in version 3.5
- INDIGO framework updated to 2.0.74,
- Mojave dark appearance support added.
What's new in version 3.4
- ArtemisHSCService detection added,
- INDIGO framework updated to 2.0.73,
- Moravian Instruments CCD driver added,
- high speed/low noise mode can be used (if driver supports it),
- synchronous mode added (synchronisation of guiding pulses and captures) to preferences.
What's new in version 3.3
- INDIGO framework updated to 2.0.68,
- list of manually added INDIGO services is persistent now.
What's new in version 3.2
To see a new video tutorial, please visit https://youtu.be/y_ZIiP5caOA
- driver stack and INDI support are completely reimplemented and replaced by INDIGO framework,
- embedded INDIGO control panel added,
- streaming is supported fast cameras (ASI and IIDC) and
- FITS based imaging component is replaced by more generic one accepting JPEG and various raw formats as well.
Please note, that AstroGuider contains many INDIGO drivers, but none of them is loaded by default. To enable the driver you actually need, select it on Preferences → INDIGO Drivers pane. You may need to scroll down to find some of them.
Initial setup and preferences
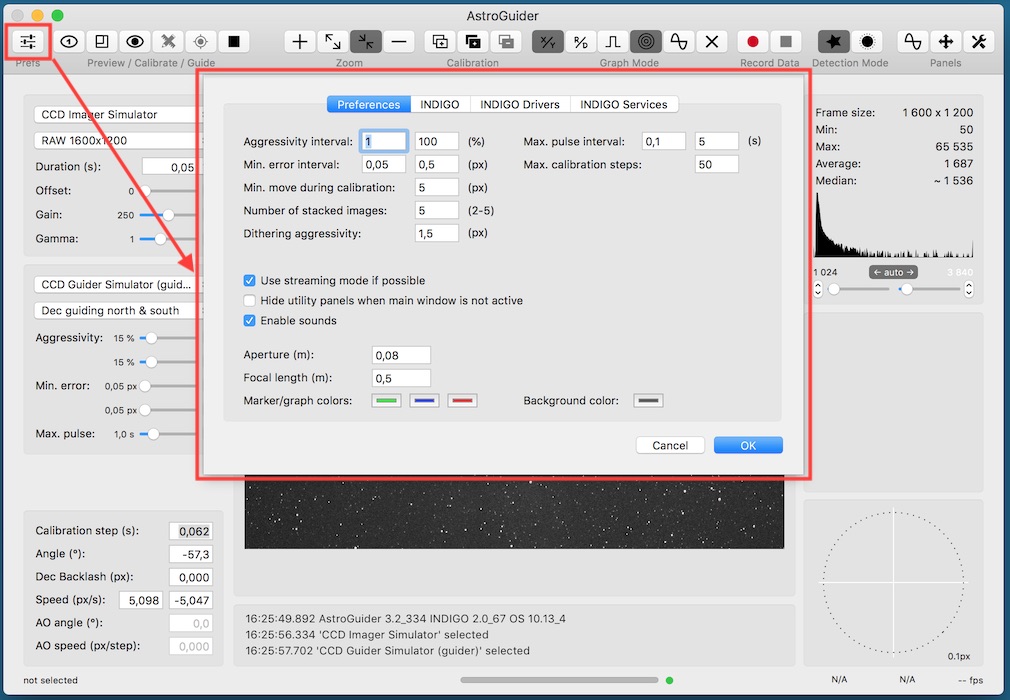
When AstroGuider is started for the first time or when button in toolbar is clicked, preferences panel is shown. It has four different panes. On the first one there are general settings and the rest is related to INDIGO framework.
Most of options on the first page is self-explaining. Aperture and Focal length values are used only for pixels to acrsecs transformation.
Port number, Bonjour service name and Bonjour service type are parameters for configuration of internal INDIGO server. Do not change them unless you understand how INDIGO works. If something will go wrong you can try to set Log level to debug or trace to see more verbose output from INDIGO framework.
AstroGuider will connect to any INDIGO server in the local network automatically, but if you want to configure connection to a service without Bonjour support (e.g. linux based INDI server or INDIGO server outside local network), you can do it on INDIGO Services pane.
Camera panel, operations and state
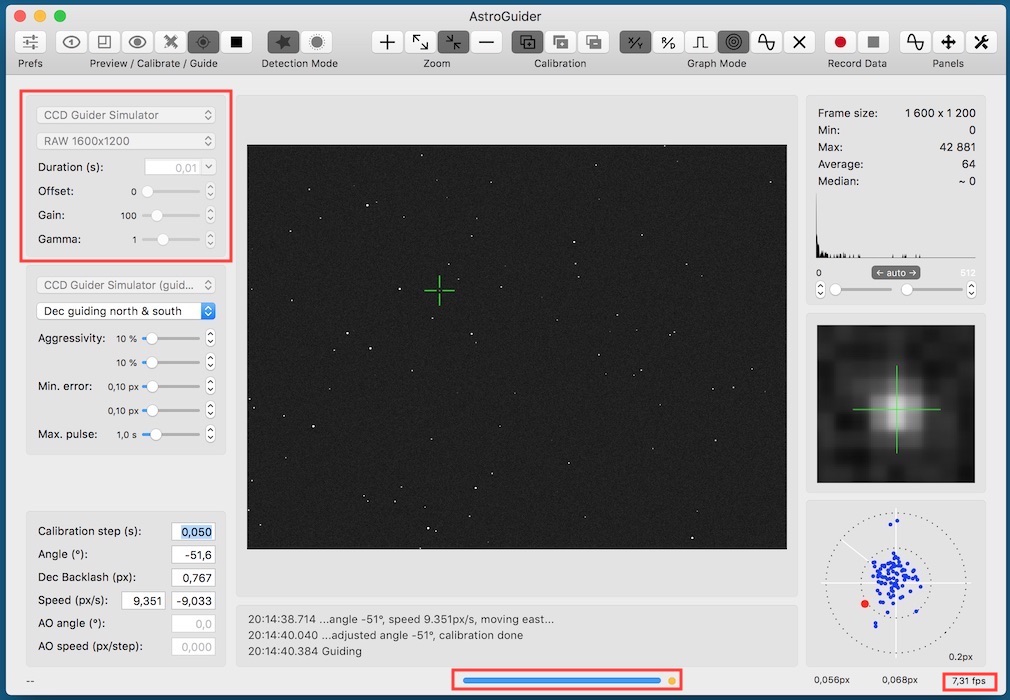
On the camera panel you can select an active camera and configure parameters for its driver:
- frame type,
- camera mode,
- duration,
- offset,
- gain and
- gama.
Camera mode represents binning, colour mode and/or bits/pixel settings of the camera.
Not every parameter can be configured for every device (e.g. Gain or Gamma) and not every parameter can be configured from the camera panel (e.g. advanced or device specific parameters). For these parameters you need to use INDIGO or INDI control panel instead while AstroGuider is running and device is connected. Make sure that you saved the configuration before closing control panel (configuration control property in main group).
The camera related operations represented by the toolbar buttons are:
- capture and display single frame,
- set/clear capture and display single frame (select rectangle on the image to set or clear subframe),
- capture and display frames in endless loop,
- calibrate (camera, guider device and suitable star should be selected)
- guide (camera, guider device and suitable star should be selected and calibrated) and
- stop all captures.
The buttons are enabled only if camera is selected.
In the status bar there are two groups of indicators related to the active camera. The first one, in the middle, shows remaining time and state of capture and the second one current FPS.
Guider panel, operations and state
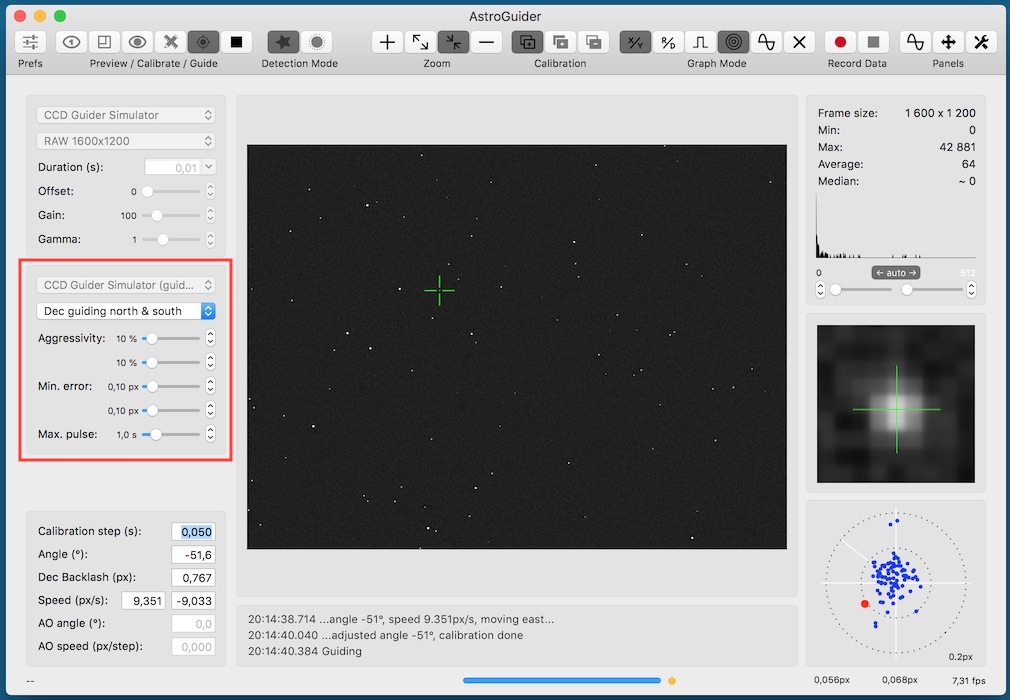
On the guider panel you can select an active guider and configure other parameters:
- guiding mode,
- guiding aggressivity ra/dec,
- min error ra/dec and
- max guiding pulse duration.
Use "Dec guiding north & south" in general case and "Dec guiding north only" or "Dec guiding south only" to compensate just bad polar alignment.
"Dec guiding disabled" should be used for mounts allowing RA guiding only (AstroTrac, SW Star Adventurer, etc.).
Calibration panel, operations and state
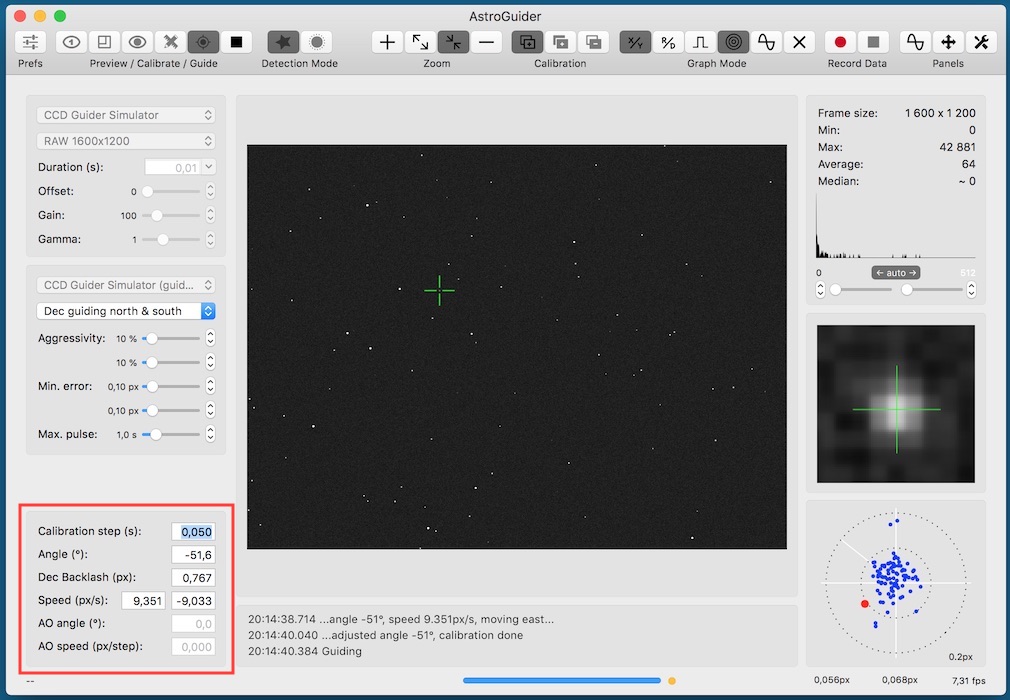
On the calibration panel you can see or set manually calibration parameters:
- calibration step,
- guider camera angle,
- dec backlash (in pixels)
- speed (in pixels/second and
- AO angle and speed.
You don't need to set any of the parameters manually, all of them are determined automatically during calibration proces.
AO support is not enabled in version as far as there is no AO driver yet, but will be available soon (e.g. StarlightXpress AO LF).
Image, histogram and detail panels
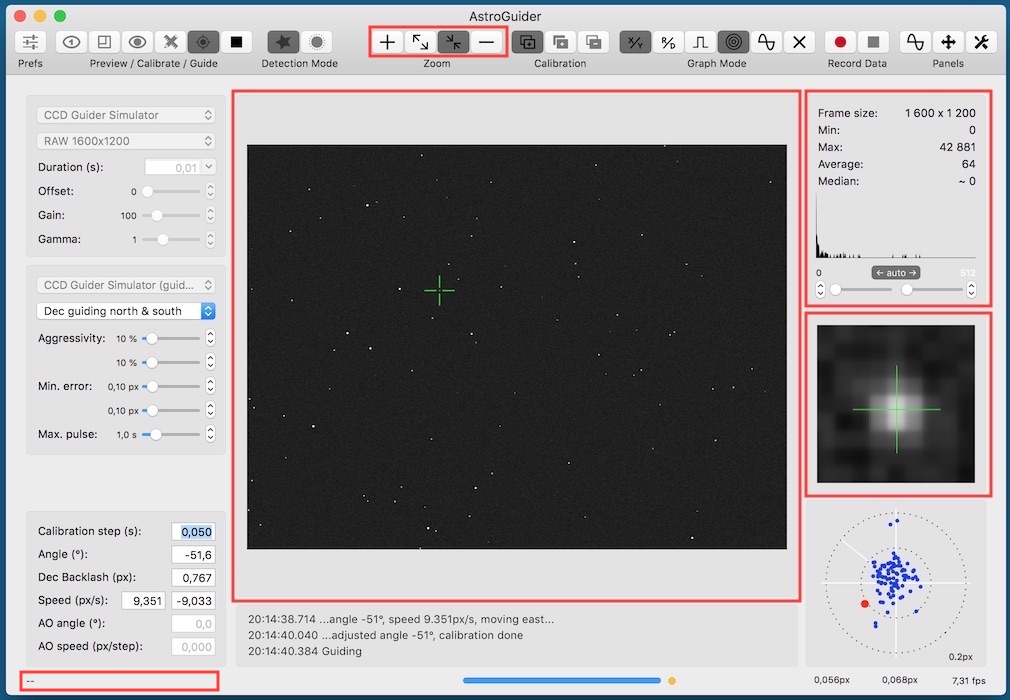
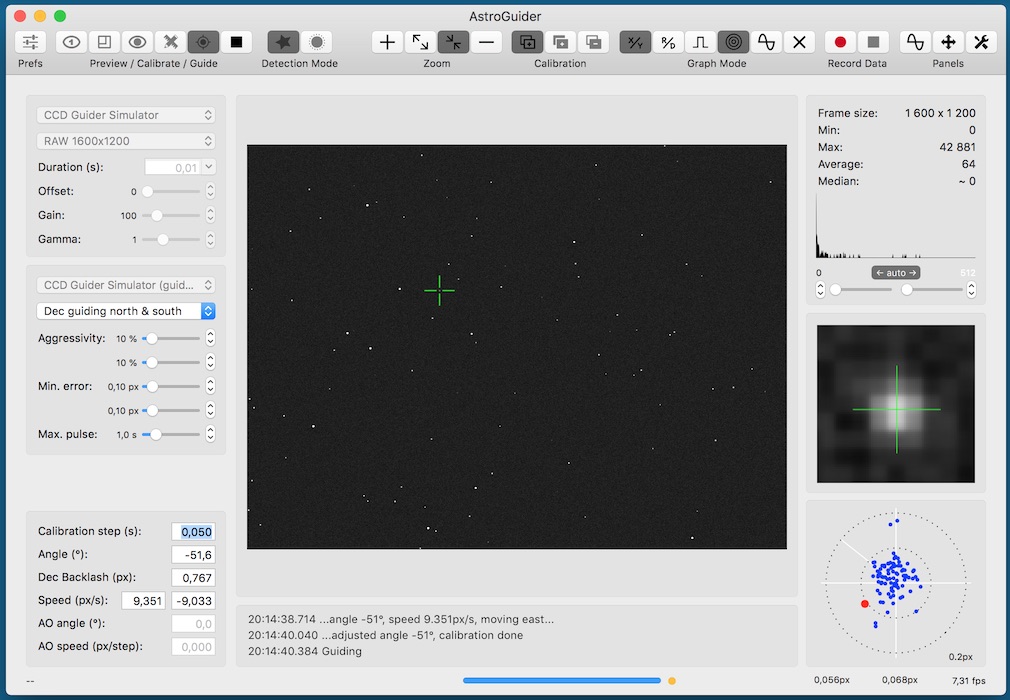
The image preview panel shows the last image captured by the camera.
If you move the mouse cursor over the image, coordinates and intensity or RGB values are shown in status bar.
If you click the position in the image, the nearest star is found and selected (marked by the green cross). This position is also used to display enlarged detail of the image and drift measurement during calibration or guiding.
In the histogram panel (top right) you can see among histogram in logarithmic scale, size of the image and some statistical data. Below the histogram there are sliders and steppers for setting black and white point for image stretching and also button to set the component into automatic mode.
In the image detail panel (middle right) there is magnified surrounding of the star selected in the image preview panel. Green cross marks the computed centroid of the selected star.
The image preview related operations are represented by two toolbar button groups. In zoom settings group there is
- zoom in,
- zoom to full size,
- zoom to fit and
- zoom out.
Other operations related to preview panel and available from view menu are show/hide crosshair reticle, set/remove guide lines #1 and set/remove guide lines #2. To set/remove guide lines select or deselect (by right mouse click) star and select operation from the menu. The setting is persistent, so you can use it to align current view with some another image.
Graph panel and graphs helper panel
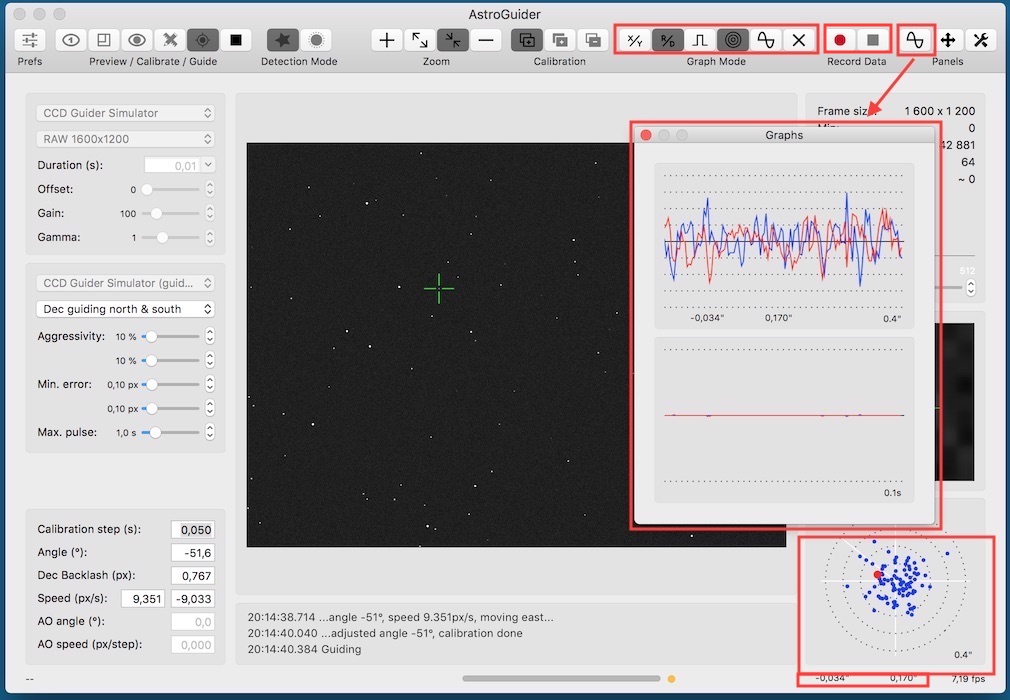
The graph panel (bottom right) shows drift (in pixels or arcseconds) or guiding pulses in linear or circular graph depending on mode selected by toolbar buttons. You can also show graphs helper panel showing drift and pulses on longer time base.
In status bar there is computed RMS error in pixels or arcseconds for RA and dec.
The scale of the graph is adjusted automatically. Blue curve represents drift in X/RA and red curve in Y/dec direction. Solid line in scale represents unit while dotted line tenths of unit.
Please note, that the graph is cleared every time you select the star in the preview image. You can do it also manually with the toolbar button.
All data can be recorded for a further analysis in CSV format readable e.g. by Excel.
Solar detection mode
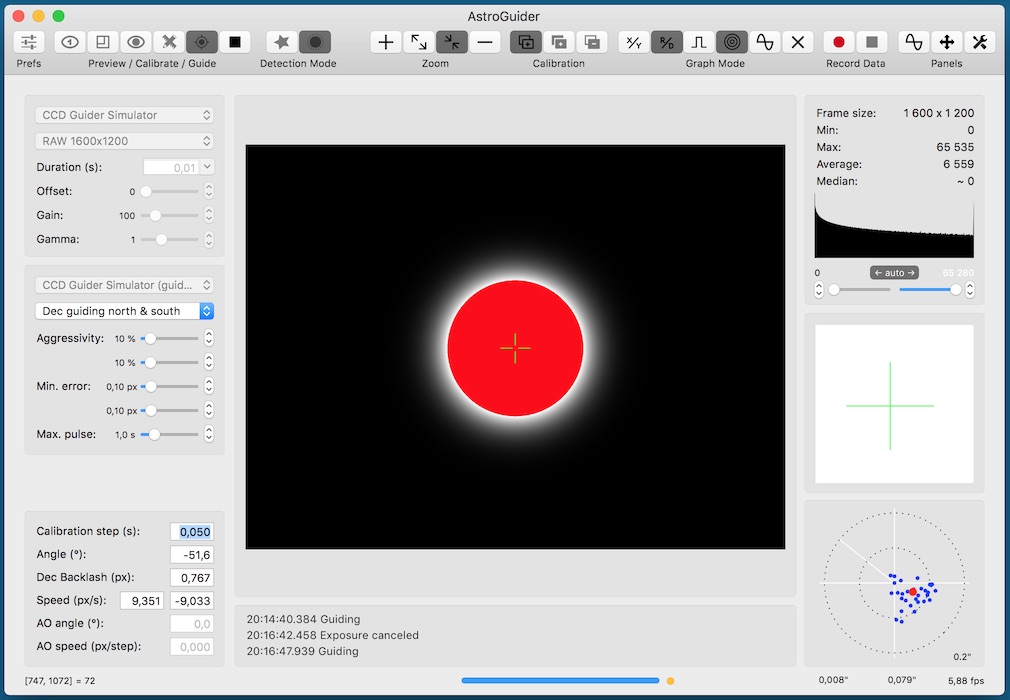
Solar mode can be also used among standard star detection mode. It will compute centroid of the whole frame instead of selected star neighbourhood.
This mode can be used for guiding during solar, lunar or planetary astrophotography session. Eclipse mode was omitted from version 3.2.
The same proceduce can be used for the calibration and guiding as if star mode is selected.
INDIGO control panel
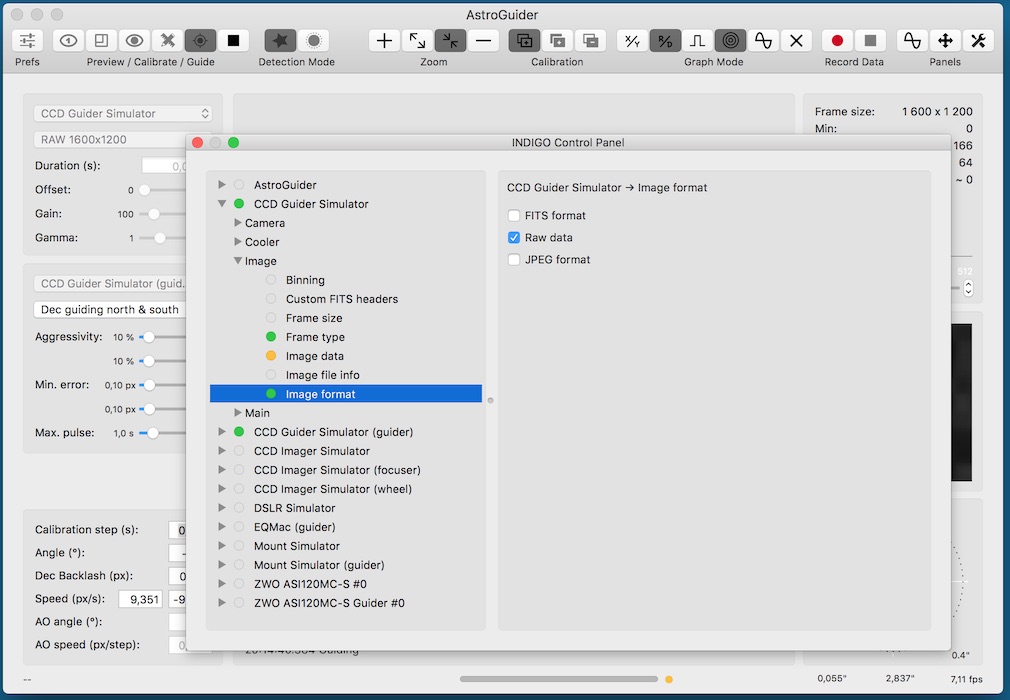
AstroGuider has a built-in control panel for managing all INDIGO or INDI devices found on the local INDIGO bus. You can expand a device → group → property tree to examine or set items of any device property.
Remember to save your changes each time you customise any settings (navigate to device → Main → Configuration control and click Save)
Distributed setups
As far as AstroGuider is based on INDIGO, it can natively use distributed setup, e.g. to control device driver running within other application or on another machine. INDIGO uses bonjour service discovery, so you don't need to configure anything while both AstroDSLR and the remote server are running on machines connected to the same local network. Otherwise you need to add hostname and port of INDIGO service to the list at INDIGO Services tab in Preferences.
Typical example of distributed setup is INDIGO server running on RaspberryPI controlling mounts and cameras in the observatory or your backyard, while AstroGuider runs on Mac computer somewhere in warm room. Another example is INDI driver executed by AstroGuider as external driver (in this case INDI driver itself acts as a server, just communicating over pipes instead of the network).
You can download INDIGO for various linux platforms (including INDIGO server and device drivers) from www.indigo-astronomy.org. If you want to use Mac computer as remote server, you can use INDIGO Server for macOS.
Device detected by remote servers appears in the list of available devices the same way as local device, just with '@ server' suffix in the name (e.g. 'Titan @ rpi.local').
To setup properties of local or remote devices not managed directly by AstroGuider (e.g. filter names, serial port device names etc.) you can use INDIGO Control Panel. Remember to save the configuration of the device driver (each device has Options section with Configuration page).
Optional INDI driver pack
If your device isn't supported by INDIGO, but has INDI driver ported to Mac computers, you can use it with optional INDI driver pack. These drivers can’t be bundled with AstroGuider due to GPL license, but you can download and install them yourself.
Source code of these drivers is available from INDI github repository.
Debugging the application
AstroGuider has a built-in debugging support for case that something went wrong. On AstroGuider → Preferences → INDIGO set "log level" to "trace", restart AstroGuider, repeat failed operation, save the log to a text file by Control → Save log and send the file to info@cloudmakers.eu for further analysis.
Further questions?
Please contact us at info@cloudmakers.eu or bb.cloudmakers.eu.